What I learned
Why O_APPEND is needed: multiple process write the same file
- Before each write(2), the file offset is positioned at the end of the file, as if with lseek(2).
- The modification of the file offset and the write operation are performed as a single atomic step.
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
It will clear all file status flags firstly.
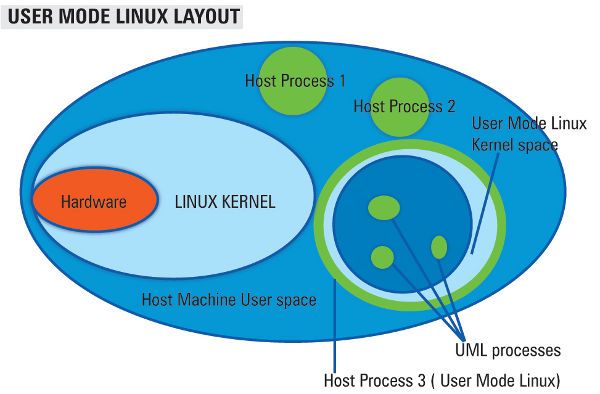
UML: user mode linux
With it, we could GDB linux system call.
CSDN: UML(User Mode Linux) – built binaries
阿里云: User mode Linux – self generate
file operation: write
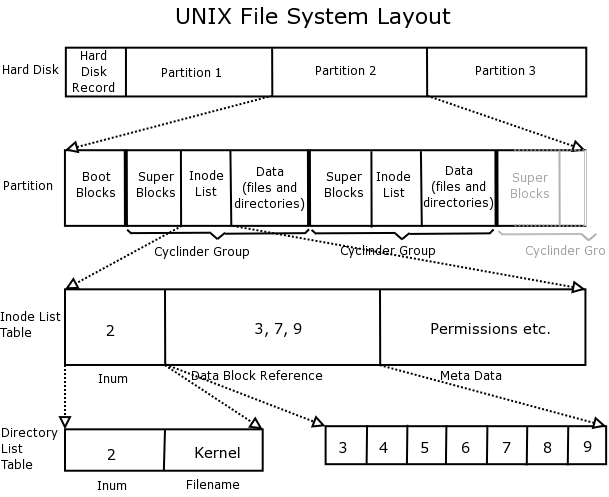
file system layout
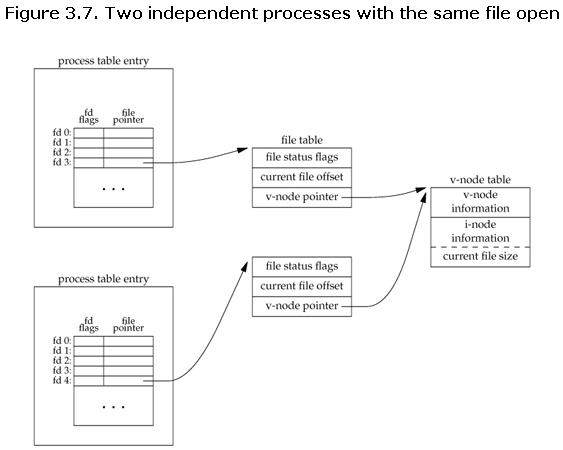
multiple process write the same file
This figure could explain why O_APPEND is needed.
SYSTEM call
If fcntl() is called, file flags will be cleared and set with the new arg
CLICK ME: [code]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(fcntl, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd, unsigned long, arg)
{
struct file *filp;
filp = fget_raw(fd);
err = do_fcntl(fd, cmd, arg, filp);
}
static long do_fcntl(int fd, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg,
struct file *filp)
{
switch (cmd) {
// ...
case F_SETFD:
err = 0;
set_close_on_exec(fd, arg & FD_CLOEXEC);
break;
case F_SETFL:
err = setfl(fd, filp, arg);
break;
// ...
}
}
#define SETFL_MASK (O_APPEND | O_NONBLOCK | O_NDELAY | O_DIRECT | O_NOATIME)
static int setfl(int fd, struct file * filp, unsigned long arg)
{
struct inode * inode = filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode;
int error = 0;
/*
* O_APPEND cannot be cleared if the file is marked as append-only
* and the file is open for write.
*/
// [GDB] b setfl if strncmp(filp->f_path->dentry->d_iname, "access", 6) == 0
if (((arg ^ filp->f_flags) & O_APPEND) && IS_APPEND(inode)) // to confirm ...
return -EPERM;
/* O_NOATIME can only be set by the owner or superuser */
if ((arg & O_NOATIME) && !(filp->f_flags & O_NOATIME))
if (!inode_owner_or_capable(inode))
return -EPERM;
/* required for strict SunOS emulation */
if (O_NONBLOCK != O_NDELAY)
if (arg & O_NDELAY)
arg |= O_NONBLOCK;
if (arg & O_DIRECT) {
if (!filp->f_mapping || !filp->f_mapping->a_ops ||
!filp->f_mapping->a_ops->direct_IO)
return -EINVAL;
}
if (filp->f_op && filp->f_op->check_flags)
error = filp->f_op->check_flags(arg);
if (error)
return error;
/*
* ->fasync() is responsible for setting the FASYNC bit.
*/
if (((arg ^ filp->f_flags) & FASYNC) && filp->f_op &&
filp->f_op->fasync) {
error = filp->f_op->fasync(fd, filp, (arg & FASYNC) != 0);
if (error < 0)
goto out;
if (error > 0)
error = 0;
}
spin_lock(&filp->f_lock);
filp->f_flags = (arg & SETFL_MASK) | (filp->f_flags & ~SETFL_MASK); // the key point ...
spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock);
out:
return error;
}
|
Append only mode
chattr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
NAME
chattr - change file attributes on a Linux file system
SYNOPSIS
chattr [ -RVf ] [ -v version ] [ mode ] files...
DESCRIPTION
The format of a symbolic mode is +-=[aAcCdDeijsStTu].
The operator '+' causes the selected attributes to be added to the existing attributes of the files; '-' causes them to be removed; and
append only (a), no atime updates (A), compressed (c), no copy on write (C), ...
|
lsattr and example
chattr to set file attribute, lsattr to show.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
x~/docker/test$ ll access.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 userA eng 168 Sep 3 16:11 access.log
x~/docker/test$ chattr +a access.log
chattr: Operation not permitted while setting flags on access.log
x~/docker/test$ sudo chattr +a access.log
x~/docker/test$ ll access.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 userA eng 168 Sep 3 16:11 access.log
~/docker/test$ lsattr access.log
-----a---------- access.log
|
UML: user mode linux
This figure depicts a conceptual layout of UML in relation to the hardware, host kernel and user-space.
GDB with UML
- 运行UML并确认其对应的进程
打开一终端,使用./linux ubda=../Debian-Wheezy-AMD64-root_fs mem=256m命令运行起UML后,再打开另一终端,并运行 ps uf | grep linux | grep -v grep | grep -v git 命令,会有如下输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
userA@slam:~$ ps uf | grep linux | grep -v grep | grep -v git
userA 7160 4.2 1.7 276996 36476 pts/5 S+ 16:05 0:17 \_ ./linux ubda=../Debian-Wheezy-AMD64-root_fs mem=256m
userA 7167 0.0 1.7 276996 36476 pts/5 S+ 16:05 0:00 \_ ./linux ubda=../Debian-Wheezy-AMD64-root_fs mem=256m
userA 7168 0.0 1.7 276996 36476 pts/5 S+ 16:05 0:00 \_ ./linux ubda=../Debian-Wheezy-AMD64-root_fs mem=256m
userA 7169 0.0 1.7 276996 36476 pts/5 S+ 16:05 0:00 \_ ./linux ubda=../Debian-Wheezy-AMD64-root_fs mem=256m
userA 7170 0.0 0.0 15528 972 pts/5 t+ 16:05 0:00 \_ ./linux ubda=../Debian-Wheezy-AMD64-root_fs mem=256m
...
|
从上面的输出内容可知对应主进程的PID为7160。
- 连接调试
使用GDB连接上已运行的UML环境并进行调试尝试。在新打开的另一终端输入如下命令:
在上面的(gdb)后面运行指令set follow-fork-mode parent,确保等会gdb一直在该进程,即在fork创建新的子进程后继续调试父进程,子进程不受影响。
接下来,在(gdb)后面继续运行指令break sys_clone创建一个断点,此时会输出如下内容:
1
2
|
(gdb) break sys_clone
Breakpoint 1 at 0x6003526d: file kernel/fork.c, line 1679.
|
接下来在运行起来的UML里输入命令ls -l,会有如下内容输出:


